News
-

Millions of Indonesians use Chinese medication to tackle wide variety of symptoms
Lily Heru and her husband always use traditional Chinese medicines when they are not feeling well. The well-educated couple, who run a textile and garment store in West Jakarta, Indonesia, use the Lian Hua TCM herbal medication for headaches, sore throats, coughs and also to relieve fatigue after a stressful day.Aug 5,2022 -

TCM law helps spur its development
The establishment of the law on traditional Chinese medicine five years ago has effectively addressed prominent barriers that used to constrain the development of TCM, officials said on Tuesday.Aug 1,2022 -
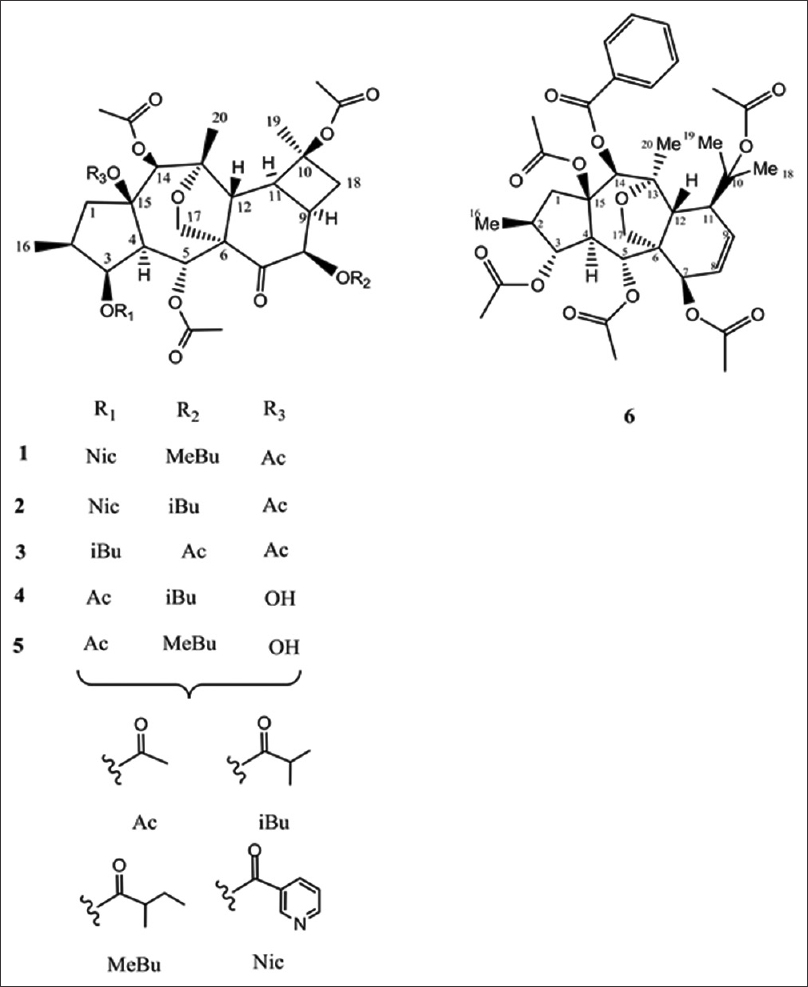
Cytotoxicity and apoptosis assay of novel cyclomyrsinol diterpenes against breast cancer cell lines
Background: Cyclomyrsinane diterpenes especially those extracted from various Euphorbia species have shown interesting biological properties in recent years.Jul 21,2022 -
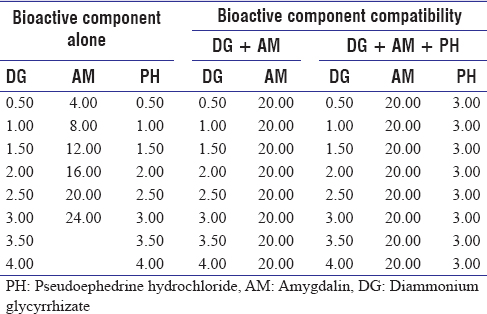
Relaxant effect of bioactive component compatibility of San-ao decoction on In vitro guinea pig airway smooth muscle: A dose-response relationship study
Background: Component compatibility is important to the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine. Studies have shown that San-ao decoction (SAD) can treat respiratory diseases by relaxing airway smooth muscle (ASM) and reducing airway hyper-responsiveness. However, whether its bioactive components and compatibility also present with similar relaxant effects remains unknown.Jul 21,2022 -
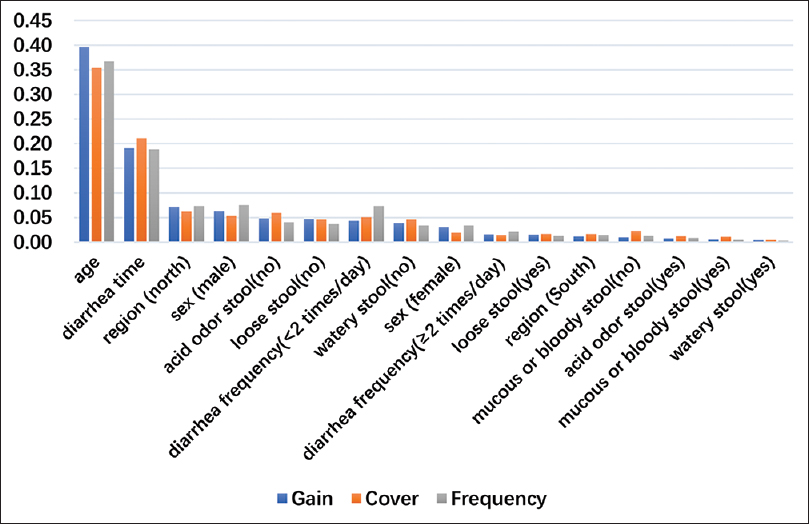
Predicting the 7th day efficacy of acupoint application of Chinese herbs (Xiao Zhong Zhi Tong Tie) in patients with diarrhea – A machine-learning model based on XGBoost algorithm
Objective: Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) was used to predict the 7th day efficacy of the acupoint application (AP) of Chinese herbs (Xiao Zhong Zhi Tong Tie) in patients with diarrhea.Jul 21,2022 -

TCM awareness abroad grows
Traditional Chinese Medicine is growing in recognition internationally and has become an important Chinese cultural symbol, senior officials said on Tuesday.Jul 19,2022

